| The algorithms of APS 3.0 used for Time Series Prediction
allow not only the evolution of models but also the use of these models to
make predictions. And
you make predictions in the Predictions Panel.
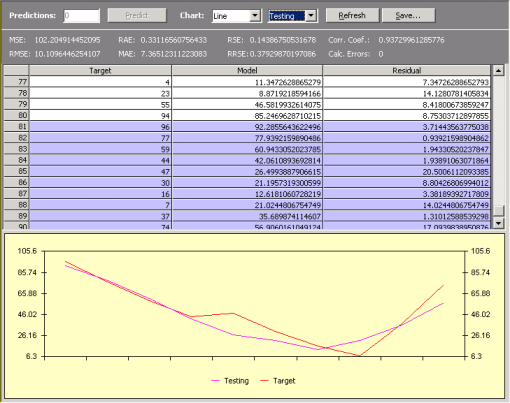
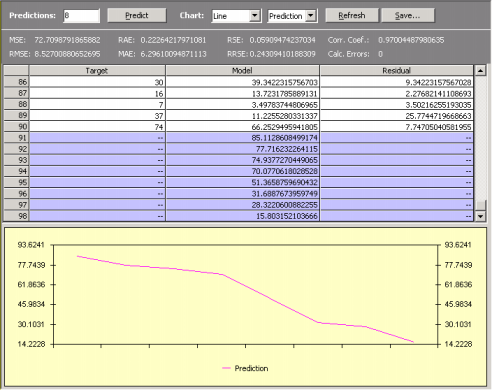
APS 3.0 allows you to make two kinds of predictions: one for testing past known events and another for making predictions about the future. In both cases, though, predictions are made recursively, by evaluating the forecast at
t+1, then using it to forecast t+2, and so on.
The second type is used obviously to predict unknown behavior, and APS 3.0 allows you to venture into the future as far as you see fit, by setting the number of predictions you want to make and then click the Predict button.
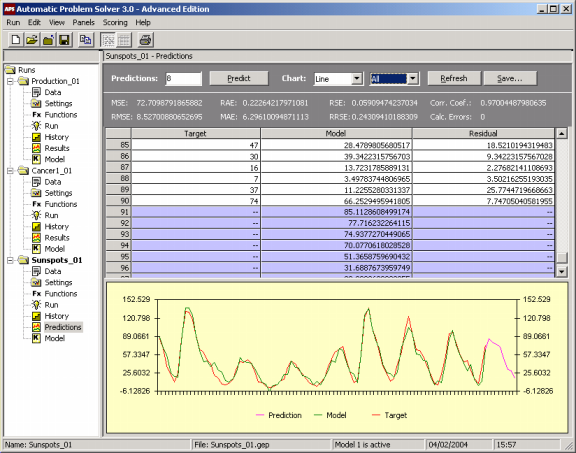
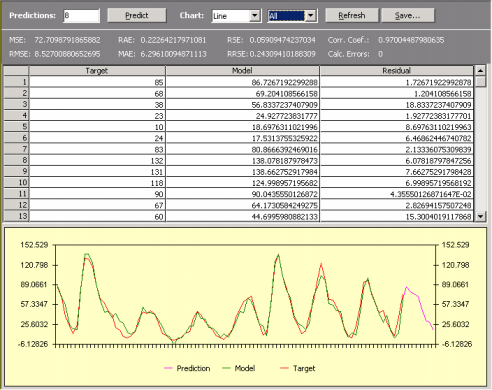
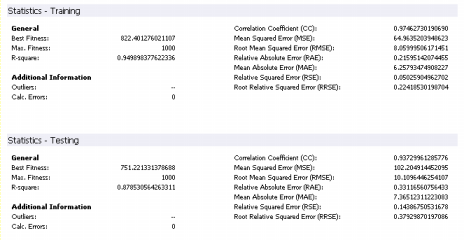
Furthermore, on the Predictions Panel, you can analyze the performance of your model in the training set and compare its output with the actual values using both a spreadsheet and a chart.
The charts of APS 3.0 come in various flavors, and you can choose Line, Area, 3D Line, and 3D Area for analyzing your model. You can also choose to plot only the output of your model, or the target values, or the predictions (either testing or real ones, depending on the option previously chosen).
|