|
Home
APS
Downloads
Buy APS
Support
Register
Contact us
Knowledge Base of APS
Subscribe to the GEPList
Visit GEP
|
|
The APS Environment
|
|
| Optimizing a Model Evolved by APS |
| |
In order to optimize a model with APS 3.0, first you must either evolve one or enter an existing model through the
Change
Seed window (see
the chapter Evolution
from Existing Models).
Automatic Problem Solver 3.0 offers three different ways of optimizing an existing model. Follow the next steps to explore all of them.
To Optimize a Model Previously Evolved by APS 3.0
- In the Run Panel, click the Optimize button.
This is the simplest way of optimizing a model using APS 3.0. This can be done for as long as you wish or until the system seems to have stopped evolving.
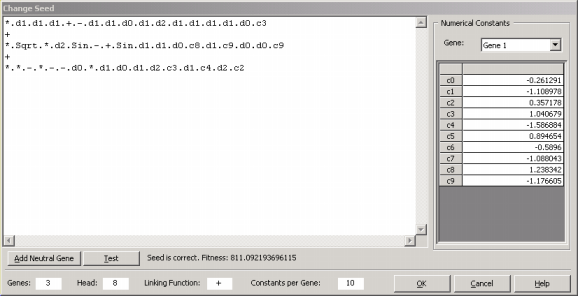
- Go to the Edit Menu and choose Change
Seed.
The second simplest way of optimizing a model using APS 3.0 is through the introduction of an additional neutral gene.
- In the Change Seed dialog box, click Add Neutral Gene.
You will see a neutral gene being added to your model. Neutrality is important for an efficient evolution and, by introducing a neutral gene, you are giving the learning algorithm more room to play and, hopefully, a better, more complex program will evolve.
- In the Run Panel, click the Optimize button.
Automatic Problem Solver 3.0 will hopefully transform the neutral gene into a significant term of your model. Again, you can repeat this strategy until the system stops responding.
- For the third method, again go to the Edit Menu and choose Change
Seed.
The last not so simple way of optimizing a model using APS 3.0 is through the direct modification of the seed. For instance, you can replace any node
(function or terminal) in the head by another and any terminal in the tail by another terminal; you can also fine-tune a numerical constant in your seed; and so forth. But if your modifications are worse that the original model, they will most probably be lost in the evolutionary process.
|
|
| Home | Contents |
Previous | Next
|
|