| |
 |
 |
 |
Last update: February 19, 2014
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Negative Predictive Value
The negative predictive value is widely used in medicine and consists of
the percentage of people with a negative diagnostic test who do not have the disease.
More formally, the negative predictive value NPVi of an individual model
i is evaluated by the equation:
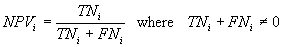
where TNi and
FNi represent, respectively, the number
of true negatives and false
negatives.
True positives (TP), true negatives (TN),
false positives (FP), and false negatives (FN), are the four
different possible outcomes of a single prediction for a
binomial classification task with classes “1” (“yes”) and “0” (“no”). A
false positive is when the outcome is incorrectly classified as “yes” (or “positive”),
when it is in fact “no” (or “negative”). A
false negative is when the outcome is incorrectly classified as negative when
it is in fact positive.
True positives and true negatives are obviously correct classifications.
These four types of classifications are usually shown in a two-way table called the
confusion matrix.
See Also:
Related Tutorials:
Related Videos:
|
|
|
|
|

