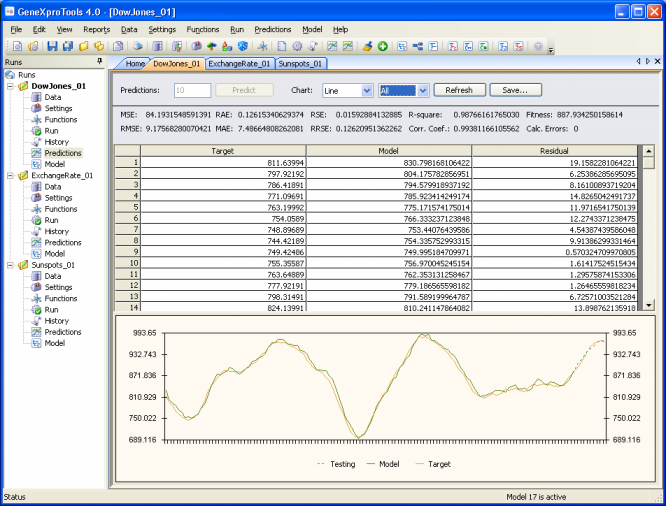
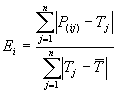|
The relative absolute error is very similar to the relative squared error in the sense that it is also relative to a simple
predictor, which is just the average of the actual values. In this case, though, the error is just the total absolute error instead of the total squared error. Thus, the relative absolute error
takes the total absolute error and normalizes it by dividing by the
total absolute error of the simple predictor. Mathematically, the relative absolute error Ei of an individual program i is evaluated by the equation:
where P(ij) is the value predicted by
the individual program i for sample case j (out of n
sample cases); Tj is the target value for sample case
j; and
For a perfect fit, the numerator is equal to 0 and Ei
= 0. So, the Ei index ranges from 0 to infinity, with 0
corresponding to the ideal.
|