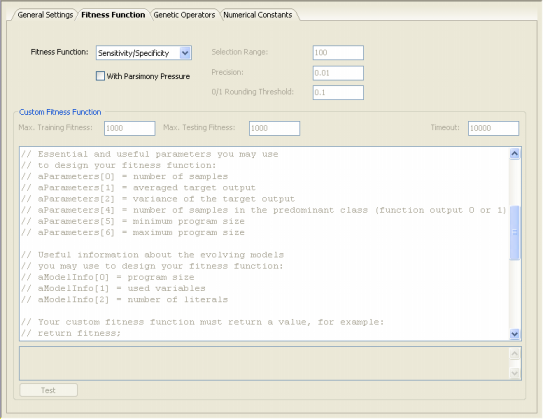
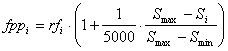| GeneXproTools 4.0 implements the Number of Hits
fitness function both with and
without parsimony pressure. The
version with parsimony
pressure puts a little pressure on the size of the evolving
solutions, allowing the discovery of more compact models.
The Number of Hits fitness function is very simple and highly efficient, and is based on the number of samples correctly classified. fi = h where h is the number of fitness cases correctly evaluated (number of
hits). fmax = n where n is the number of fitness cases.
where Si is the size of the program, Smax and Smin represent, respectively, maximum and minimum program sizes and are evaluated by the formulas: Smax = G (h + t) Smin = G where G is the number of genes, and h and t are the head and tail sizes (note that, for simplicity, the linking function was not taken into account). Thus, when rfi = rfmax and Si = Smin (highly improbable, though, as this can only happen for very simple functions as this means that all the sub-ETs are composed of just one node), fppi = fppmax, with fppmax evaluated by the formula:
|