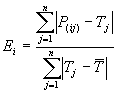| The relative absolute error fitness function (RAE) of APS 3.0 is, as expected, based on the standard
relative absolute error. The relative absolute error Ei of an individual program i is evaluated by the equation:
where P(ij) is the value predicted by
the individual program i for fitness case j (out of n
fitness cases); Tj is the target value for fitness
case j; and
For a perfect fit, the numerator is equal to 0 and Ei
= 0. So, the RAE index ranges from 0 to infinity, with 0
corresponding to the ideal.
which obviously ranges from 0 to 1000, with 1000 corresponding to the ideal (the coefficient 1000 allows a fairer distribution of fitnesses for selection). |